News Release 11-147
Diamond Impurities Bonanza for Geologists Studying Earth's History
Ancient minerals tell story of planet's distant past
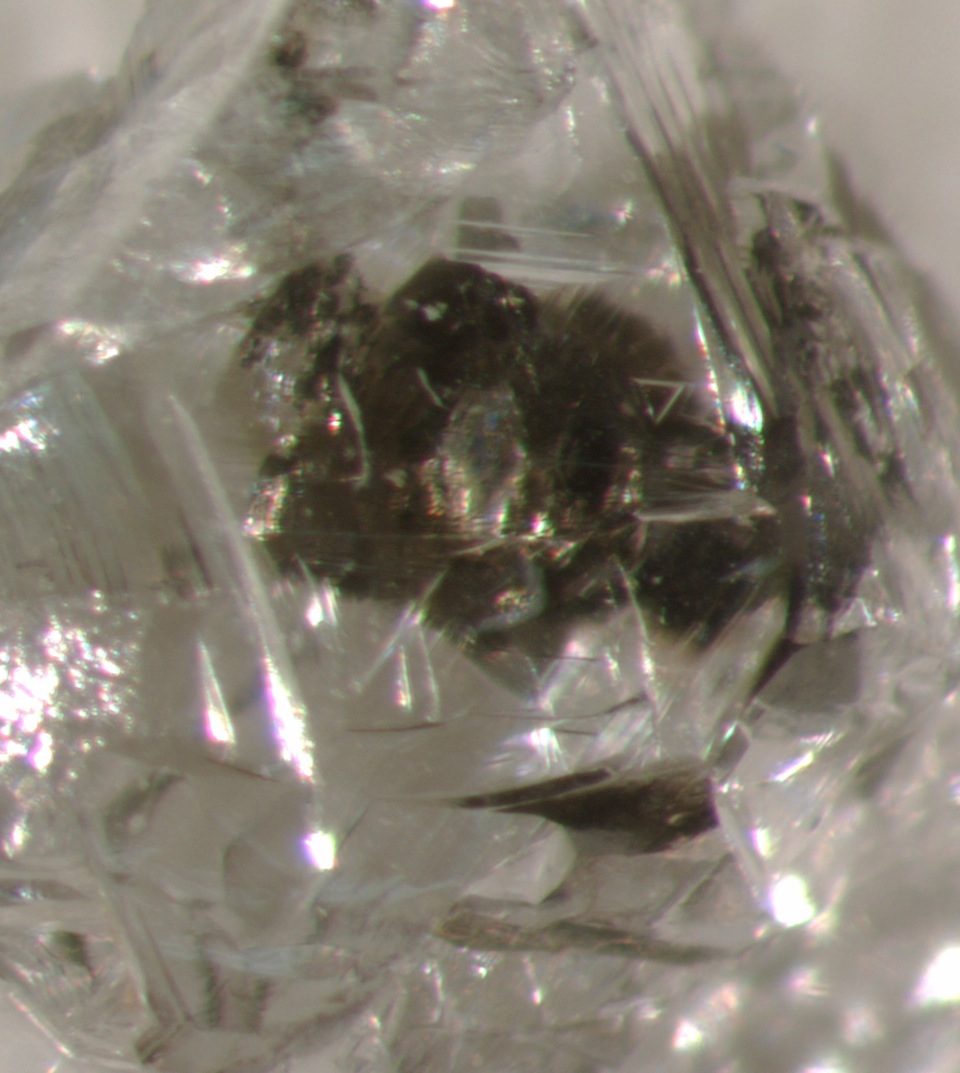
Optical photomicrograph of a sulfide-inclusion-bearing rough diamond from Botswana.
July 21, 2011
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.
Jewelers abhor diamond impurities, but they are a bonanza for scientists.
Safely encased in super-hard diamond, impurities are unaltered, ancient minerals that tell the story of Earth's distant past.
Researchers analyzed data from more than 4,000 of these mineral inclusions to find that continents started the cycle of breaking apart, drifting, and colliding about three billion years ago.
The research results, published in this week's issue of the journal Science, pinpoint when this so-called Wilson cycle began.
Lead author Steven Shirey of the Carnegie Institution's Department of Terrestrial Magnetism says that the Wilson cycle is responsible for the growth of the Earth's continental crust, the continental structures we see today, the opening and closing of ocean basins through time, mountain building, and the distribution of ores and other materials in the crust.
"But when it all began has remained elusive until now," Shirey says.
"We used the impurities, or inclusions, contained in diamonds, because they are perfect time capsules from great depth beneath the continents.
"They provide age and chemical information for a span of more than 3.5 billion years that includes the evolution of the atmosphere, the growth of the continental crust, and the beginning of plate tectonics."
Co-author Stephen Richardson of the University of Cape Town says that it's "astonishing that we can use the smallest mineral grains that can be analyzed to reveal the origin of some of Earth's largest geological features."
"The tiny inclusions found inside diamonds studied by this team have recorded the chemistry and evolution of the Earth over 3.5 billion years," says Jennifer Wade, program director in the National Science Foundation (NSF)'s Division of Earth Sciences, which funded the research. "They help pinpoint when the cycle of plate tectonics first began on Earth."
The largest diamonds come from cratons, the most ancient formations within continental interiors that have deep mantle roots or keels around which younger continental material gathered.
Cratons contain the oldest rocks on the planet, and their keels extend into the mantle more than 125 miles where pressures are sufficiently high, but temperatures sufficiently low, for diamonds to form and be stored for billions of years.
Over time, diamonds have arrived at the surface as accidental passengers during volcanic eruptions of deep magma that solidified into rocks called kimberlites.
The inclusions in diamonds come in two major varieties: peridotitic and eclogitic.
Peridotite is the most abundant rock type in the upper mantle, whereas eclogite is generally thought to be the remnant of oceanic crust recycled into the mantle by the subduction or sinking of tectonic plates.
Shirey and Richardson reviewed the data from more than 4,000 inclusions of silicate--the Earth's most abundant material--and more than 100 inclusions of sulfide from five ancient continents.
The most crucial aspects, they say, looked at when the inclusions were encapsulated and the associated compositional trends.
Compositions vary and depend on the geochemical processing that precursor components underwent before they were encapsulated.
Two systems used to date inclusions were compared. Both rely on natural isotopes that decay at exceedingly slow but predictable rates--about one disintegration every ten years on the scale of an inclusion--making them excellent atomic clocks for determining absolute ages.
The researchers found that before 3.2 billion years ago, only diamonds with peridotitic compositions formed, whereas after three billion years ago, eclogitic diamonds dominated.
"The simplest explanation," says Shirey, "is that this change came from the initial subduction of one tectonic plate under the deep mantle keel of another as continents began to collide on a scale similar to that of the supercontinent cycle today.
"The sequence of underthrusting and collision led to the capture of eclogite in the subcontinental mantle keel along with the fluids that are needed to make diamond."
Concludes Richardson, "This transition marks the onset of the Wilson cycle of plate tectonics."
-NSF-
-
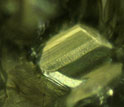
Below this diamond's surface is a hexagonal grain of iron sulfide surrounded by a black rim.
Credit and Larger Version -
The hexagonal grain of iron sulfide may be removed for analysis to reveal the diamond's age.
Credit and Larger Version -
Eclogitic diamond from the Orapa kimberlite, Botswana, shows an older diamond core.
Credit and Larger Version -
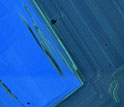
In this photo, a blue core surrounds banded diamond growth in an eclogitic diamond from Botswana.
Credit and Larger Version -
The researchers' findings are described in the July 22 issue of the journal Science.
Credit and Larger Version
Media Contacts
Cheryl Dybas, NSF, (703) 292-7734, email: cdybas@nsf.gov
Tina McDowell, Carnegie Institution for Science, (202) 939-1120, email: tmcdowell@carnegiescience.edu
The U.S. National Science Foundation propels the nation forward by advancing fundamental research in all fields of science and engineering. NSF supports research and people by providing facilities, instruments and funding to support their ingenuity and sustain the U.S. as a global leader in research and innovation. With a fiscal year 2023 budget of $9.5 billion, NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives more than 40,000 competitive proposals and makes about 11,000 new awards. Those awards include support for cooperative research with industry, Arctic and Antarctic research and operations, and U.S. participation in international scientific efforts.
Connect with us online
NSF website: nsf.gov
NSF News: nsf.gov/news
For News Media: nsf.gov/news/newsroom
Statistics: nsf.gov/statistics/
Awards database: nsf.gov/awardsearch/
Follow us on social
Twitter: twitter.com/NSF
Facebook: facebook.com/US.NSF
Instagram: instagram.com/nsfgov