Multimedia Gallery
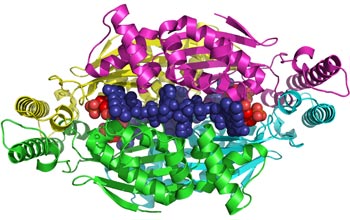
Cartoon diagram of an enzyme, an example of the class of FDTS enzymes.
Cartoon diagram of a Thermotoga maritima bacterium flavin-dependent thymidylate synthase, or FDTS, enzyme, which is an example of the class of FDTS enzymes. The FDTS enzyme is coded by the thyX gene and has been found primarily in bacteria and viruses, including several human pathogens and biological warfare agents. The two compounds involved in the active site of the enzymatic reaction, FAD and deoxy-uridine monophosphate, are represented by the small bluish-purple and red grouped spheres, respectively, and are enclosed by four protein sub-units depicted by green, light blue, gold and pink magenta ribbon-like structures.
Credit: Amnon Kohen, University of Iowa
Images credited to the National Science Foundation, a federal agency, are in the public domain. The images were created by employees of the United States Government as part of their official duties or prepared by contractors as "works for hire" for NSF. You may freely use NSF-credited images and, at your discretion, credit NSF with a "Courtesy: National Science Foundation" notation.
Additional information about general usage can be found in Conditions.
Also Available:
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (300 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
Related story: Scientists Discover New Chemical Reaction for DNA Production in Bacteria and Viruses