All Images
Research News
3-D Images Reveal New Composition of the Sun
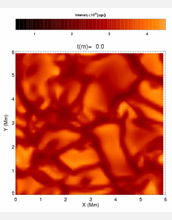
Improved 3-D simulations force scientists to reevaluate the sun's composition. Results show the amount of carbon and oxygen in the Earth's closest star is 30 to 40 percent lower than previously believed. Since the chemical make-up of the sun is a reference point for the composition of other objects in the universe, many models that relied on higher abundances are put into question. In this image of the observable surface of a star about 3,000 degrees cooler than the sun, the bright regions correspond to the "granules" of hot ascending gas, which are surrounded by "intergranular lanes" of cool material sinking back into the star's interior. View the animated image.
Credit: I. Ramirez, M. Asplund, C. Allende Prieto, L. Koesterke, D. L. Lambert.
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (127 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.


