News Release 06-043
New "Crystal Sponge" Triples Hydrogen Storage
UCLA, University of Michigan chemists advance hydrogen as fuel for cars and electronic devices
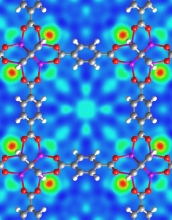
A neutron-scattering image shows hydrogen (red-green circles) bound in a MOF crystal.
March 9, 2006
This material is available primarily for archival purposes. Telephone numbers or other contact information may be out of date; please see current contact information at media contacts.
In a step toward making cars that can run on hydrogen rather than gasoline a reality, chemists at UCLA and the University of Michigan have announced a new "crystal sponge" material that can store in its pores nearly three times more hydrogen than any substance known previously.
Indeed, say UCLA chemist Omar Yaghi and his colleagues, who are scheduled to publish their findings in late March in the Journal of the American Chemical Society, this is the first material to achieve the kind of storage capacities required to make hydrogen fuel practical. The fully saturated crystal sponge is 7.5 percent hydrogen by weight.
The payoff could be hydrogen fuel that powers not only cars, but laptop computers, cellular phones, digital cameras and other electronic devices as well.
For now, notes Yaghi, the high storage densities are possible only at very low temperatures, below 77 degrees Kelvin (-321 degrees Fahrenheit). But he is optimistic the limitation is temporary.
This particular material is just one in a large class of compounds he invented in the early 1990s, Yaghi explains. Known as metal-organic frameworks (MOFs), they have a crystal structure that resembles a scaffold made of linked rods -- a structure that gives them a multitude of nanoscale pores, and a correspondingly huge internal surface area where gas molecules can attach. (A pinch of a MOF has roughly the surface area of a football field.)
But the precise details of that structure can be tailored quite easily by changing the starting materials, Yaghi says; his laboratory has already made more than 500 different MOFs over the years-few of which have even been tested for hydrogen storage. So, he believes it's possible to modify the rod-like components to store hydrogen at everyday temperatures.
This research was funded by the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Energy and BASF, a global chemical company based in Germany.
For more information see the UCLA news release.
-NSF-
Media Contacts
M. Mitchell Waldrop, NSF, (703) 292-7752, email: mwaldrop@nsf.gov
Stuart Wolpert, UCLA, (310) 206-0511, email: swolpert@support.ucla.edu
Related Websites
UCLA news release: http://newsroom.ucla.edu/page.asp?RelNum=6873
The U.S. National Science Foundation propels the nation forward by advancing fundamental research in all fields of science and engineering. NSF supports research and people by providing facilities, instruments and funding to support their ingenuity and sustain the U.S. as a global leader in research and innovation. With a fiscal year 2023 budget of $9.5 billion, NSF funds reach all 50 states through grants to nearly 2,000 colleges, universities and institutions. Each year, NSF receives more than 40,000 competitive proposals and makes about 11,000 new awards. Those awards include support for cooperative research with industry, Arctic and Antarctic research and operations, and U.S. participation in international scientific efforts.
Connect with us online
NSF website: nsf.gov
NSF News: nsf.gov/news
For News Media: nsf.gov/news/newsroom
Statistics: nsf.gov/statistics/
Awards database: nsf.gov/awardsearch/
Follow us on social
Twitter: twitter.com/NSF
Facebook: facebook.com/US.NSF
Instagram: instagram.com/nsfgov


