All Images
Research News
Monitoring and Predicting Extraterrestrial Weather

Two Hubble Space Telescope storm watch images from late June and early September 2001 offer dramatically contrasting views of the Martian surface. At left, the onset of smaller "seed" storms can be seen near the Hellas basin (lower right edge of Mars) and the northern polar cap. A similar surface view at right, taken over two months later, shows the fully developed extent of the obscuring global dust storm.
Credit: J. Bell (Cornell), M. Wolff (Space Science Inst.), Hubble Heritage Team (STScI / AURA), NASA
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (922 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.

Taken on January 14, 2005, these views show the dramatic descent of the Huygens probe to the surface of Saturn's moon, Titan, one of the most distant touchdowns ever made by a spacecraft. Part of the European Space Agency-NASA-University of Arizona effort to explore Titan, Saturn's largest moon, the images were put together with data collected by the Descent Imager/Spectral Radiometer instrument during the probe's 147-minute plunge through Titan's thick orange-brown atmosphere to a soft, sandy riverbed.
Credit: ESA/NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (275 KB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
An image of the Phoenix lander descending through the Martian atmosphere on a parachute on May 25, 2008. The image was captured by the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter HiRISE camera. Planning for spacecraft entry required detailed modeling of Martian atmospheric conditions.
Credit: NASA/JPL/University of Arizona
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (4.8 MB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
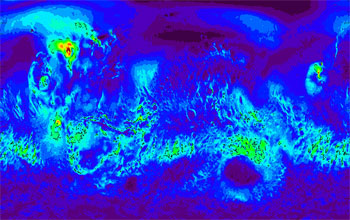
A global simulation of wind stress (i.e., how hard the wind is blowing) on the surface of Mars. Scientists studying Mars use this information to identify locations on the planet's surface where dust will likely get lifted.
Credit: NASA
Download the high-resolution JPG version of the image. (1.5 MB)
Use your mouse to right-click (Mac users may need to Ctrl-click) the link above and choose the option that will save the file or target to your computer.
